The Benefits of Binaural Hearing Aids
If you have hearing loss in both ears, you might be wondering whether

If you have hearing loss in both ears, you might be wondering whether
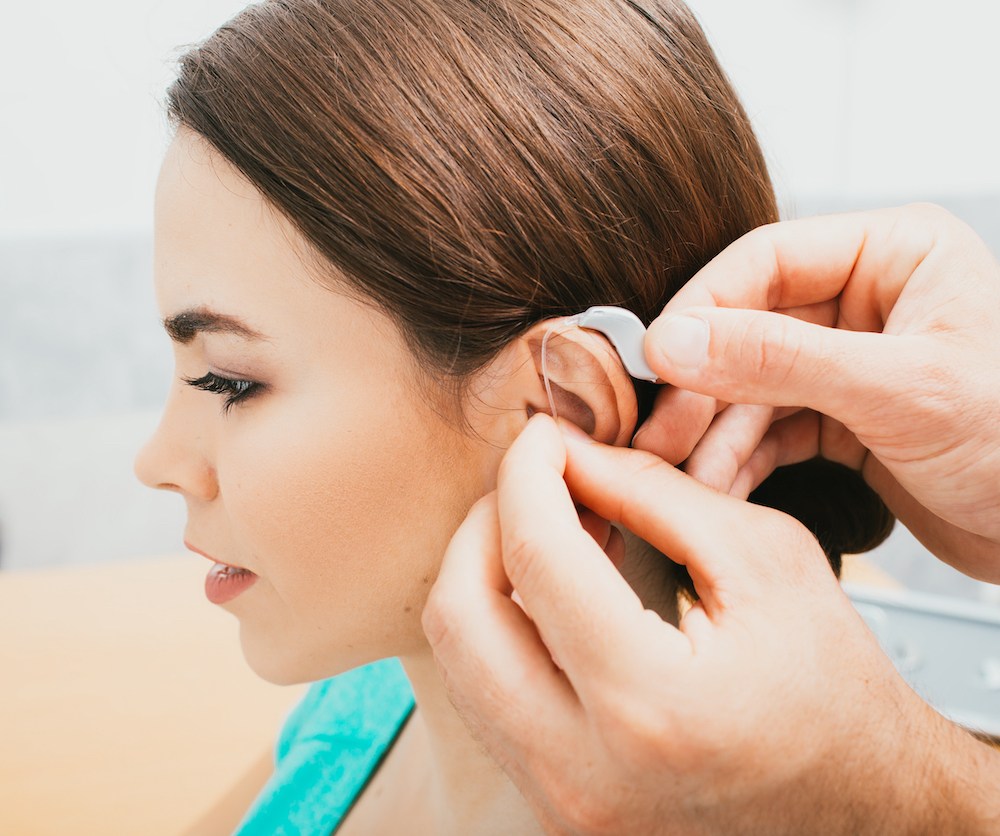

Many people notice hearing loss in one ear and wonder if both ears need

As you age, changes in hearing can make it harder to follow conversations